Mooring Systems Required: Types, Components, and Marine Safety
Mooring systems are essential components in marine operations, ensuring that vessels stay securely in place when docked or at anchor. Whether it’s a small fishing boat or a large commercial ship, the right mooring system is critical to safety and efficiency. In this post, we explore the different types of mooring systems, their components, applications, and maintenance tips.
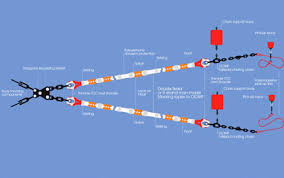
What Are Mooring Systems?
A mooring system is a combination of anchors, chains, ropes, and buoys designed to hold a vessel in a fixed position on the water. The system resists environmental forces such as wind, waves, and current. Marine operators require customized mooring solutions depending on vessel size, water depth, and seabed conditions.
Types of Mooring Systems
- Single Point Mooring (SPM): Often used in offshore operations like oil transfer.
- Spread Mooring: Common in offshore drilling platforms for stability.
- Multi-Point Mooring: Provides better hold for dynamic environments.
- Pile Mooring: Uses fixed posts embedded in the seabed.
- Buoy Mooring: Utilizes a floating buoy to anchor vessels.
Key Components of Mooring Systems
- Anchor: Grips the seabed to provide resistance.
- Chain/Rope: Connects the anchor to the vessel or buoy.
- Buoys: Helps identify anchor points and manage tension.
- Connectors/Shackles: Link all components securely.
Importance of Proper Mooring
Improper mooring can lead to drifting, collisions, and damage to marine infrastructure. Reliable systems reduce risks and comply with port and offshore safety standards. Regular inspections and maintenance ensure the mooring system performs optimally under stress.
SEANAV’s Mooring Solutions
At SEANAV, we offer complete mooring system consultations, installation, and maintenance services. Our experts analyze environmental data and vessel specifications to recommend the most secure and cost-effective mooring systems for your operations.

FAQs About Mooring Systems
1. What is the purpose of a mooring system?
To securely anchor a vessel in place and prevent unwanted movement caused by wind, waves, or currents.
2. What materials are used in mooring lines?
Materials include steel chains, nylon ropes, polyester, and synthetic fiber blends depending on strength and flexibility needs.
3. How often should mooring systems be inspected?
Regular inspections should occur every 6 to 12 months, or after extreme weather events.
4. What is a single-point mooring system?
It allows vessels to moor at a central floating buoy used mainly in offshore oil and gas operations.
5. What are mooring buoys used for?
They provide a floating anchor point for vessels, reducing strain on docks and avoiding seabed damage.
6. Can mooring systems be customized?
Yes, systems can be tailored based on vessel size, water conditions, and operational requirements.
7. How deep can a mooring system go?
Mooring systems can be designed for shallow coastal waters or ultra-deep offshore platforms exceeding 3,000 meters.
8. What role does a mooring winch play?
It controls the tension of mooring lines, especially in dynamic positioning and tidal environments.
9. Is maintenance expensive?
Preventive maintenance is more cost-effective than emergency repairs or damage from mooring failure.
10. What is dynamic mooring analysis?
A simulation to assess how a mooring system performs under changing marine forces like waves and currents.
11. How does SEANAV support mooring safety?
SEANAV provides engineering expertise, modern equipment, and ongoing support for safe and reliable mooring systems.
Contact SEANAV Today
Need assistance with mooring systems? Contact SEANAV for expert support, tailored solutions, and compliance with international marine standards. Whether you’re upgrading your mooring setup or planning a new installation, we’re here to help.


